[原创] 广告推荐算法(group auc)评价指标及Spark实现代码时间:2022-01-11 09:08:27 我们曾经有这样的疑惑,那就是训练样本,AUC得到提升。当将新模型放到线上后,却发现实际效果却没有老模型好,这时候很多人就开始疑惑了。 在机器学习算法中,很多情况我们都是把auc当成最常用的一个评价指标,而auc反映整体样本间的排序能力,但是有时候auc这个指标可能并不能完全说明问题,有可能auc并不能真正反映模型的好坏,以CTR预估算法(推荐算法一般把这个作为一个很重要的指标)为例,把用户点击的样本当作正样本,没有点击的样本当作负样本,把这个任务当成一个二分类进行处理,最后模型输出的是样本是否被点击的概率。 举个很简单的例子,假如有两个用户,分别是甲和乙,一共有5个样本,其中+表示正样本,-表示负样本,我们把5个样本按照模型A预测的score从小到大排序,得到 甲-,甲+,乙-,甲+,乙+. 那么实际的auc应该是 (1+2+2)/(32)=0.833, 那假如有另一个模型B,把这5个样本根据score从小到大排序后,得到 甲-,甲+,甲+,乙-,乙+, 那么该模型预测的auc是(1+1+2)/(32)=0.667。 那么根据auc的表现来看,模型A的表现优于模型B,但是从实际情况来看,对于用户甲,模型B把其所有的负样本的打分都比正样本低,故,对于用户甲,模型B的auc是1, 同理对于用户乙,模型B的auc也应该是1,同样,对于用户甲和乙,模型A的auc也是1,所以从实际情况来看,模型B的效果和模型A应该是一样好的,这和实际的auc的结果矛盾。 可能auc这个指标失真了,因为用户广告之间的排序是个性化的,不同用户的排序结果不太好比较,这可能导致全局auc并不能反映真实情况。 因为auc反映的是整体样本间的一个排序能力,而在计算广告领域,我们实际要衡量的是不同用户对不同广告之间的排序能力, 实际更关注的是同一个用户对不同广告间的排序能力,为此,参考了阿里妈妈团队之前有使用的group auc的评价指标 group auc实际是计算每个用户的auc,然后加权平均,最后得到group auc,这样就能减少不同用户间的排序结果不太好比较这一影响。group auc具体公式如下: 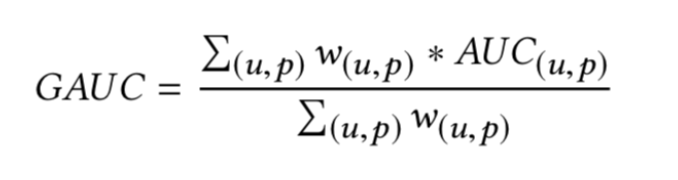 实际处理时权重一般可以设为每个用户view的次数,或click的次数,而且一般计算时,会过滤掉单个用户全是正样本或负样本的情况。 但是实际上一般还是主要看auc这个指标,但是当发现auc不能很好的反映模型的好坏(比如auc增加了很多,实际效果却变差了),这时候可以看一下gauc这个指标。 由于Spark计算AUC需要将数据转为RDD,且非常慢。如果计算每个用户的AUC将会超级花费时间。下面是我实现的一种快速计算GAUC的方式,供大家参考。 ```scala object AUCUtil { /** * 获取ROC曲线 * scoreAndLabels : _._1 is positive probability,_._2 is true label */ def roc(scoreAndLabels: Array[(Double, Double)]): Array[(Double, Double)] = { val results = scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[(Double, Double)]() val scoreAndLabelsCount = scoreAndLabels.length val scoreAndLabelsWithIndex = scoreAndLabels.seq.sortBy(_._1).zipWithIndex.map(row => { (row._2 + 1, row._1._1, row._1._2) }) val num = 20 //阀值 val thresholds = scala.collection.mutable.Set[Double]() for (a = scoreAndLabelsCount) index = scoreAndLabelsCount val threshold = scoreAndLabelsWithIndex.filter(_._1 == index)(0)._2 thresholds += threshold } //正样本的数量 val positiveCount = scoreAndLabels.filter(_._2 == 1.0).length //负样本的数量 val negativeCount = scoreAndLabels.filter(_._2 == 0.0).length results += ((0, 0)) //全是正样本和全是负样本不处理 if (positiveCount != 0 && negativeCount != 0) { val thrsholdsSorted = thresholds.toSeq.sortWith(_ > _) for (threshold row._2 == 1.0 && row._1 >= threshold).length //预测为正样本的数量 val P = scoreAndLabels.filter(_._1 >= threshold).length //负样本中预测错误的数量 val FP = scoreAndLabels.filter(row => row._2 == 0.0 && row._1 >= threshold).length //FPR val FPR = (FP.toDouble / negativeCount.toDouble).toDouble.formatted("%.5f").toDouble //TPR,召回率 val TPR = (TP.toDouble / positiveCount.toDouble).toDouble.formatted("%.5f").toDouble results += ((FPR, TPR)) } } results += ((1, 1)) results.distinct.toArray } /** * 使用梯形法则计算连接两个输入点的线下面积。 * (上底+下底)*高/2 */ def trapezoid(points: Seq[(Double, Double)]): Double = { require(points.length == 2) val x = points.head val y = points.last (y._1 - x._1) * (y._2 + x._2) / 2.0 } /** * 计算曲线下的面积 * curve : _1 is FPR,_2 is TPR */ def areaUnderROC(curve: Iterable[(Double, Double)]): Double = { curve.toIterator.sliding(2).withPartial(false).aggregate(0.0)( seqop = (auc: Double, points: Seq[(Double, Double)]) => auc + trapezoid(points), combop = _ + _) } def group_auc(predictions: DataFrame, userId: String): Double = { group_auc(predictions, userId, "probability") } /** * 二分类模型GAUC评估,使用曝光数加权 * @param predictions 测试集返回的预测结果 * @param userId 用户ID列名 * @param probabilityCol 概率值的列名 */ def group_auc(predictions: DataFrame, userId: String, probabilityCol: String): Double = { import predictions.sparkSession.implicits._ val positiveUser = predictions.where("label = 1").select(userId).distinct() val scoreAndLabels = predictions.join(positiveUser, Seq[String](userId), "leftsemi").select(col(userId).cast(StringType), col(probabilityCol), col("label").cast(DoubleType)).rdd.map(row => { val label = row.getAs[Double]("label") val id = row.getAs[String](userId) var score = row.getAs[Vector](probabilityCol)(1) (id, score, label) }).toDF(userId, "score", "label") val userCount = scoreAndLabels.select(userId).distinct().count().toInt println(s"userCount = ${userCount}") var result = scoreAndLabels.repartitionByRange(1000, col(userId)).rdd.mapPartitions({ val results = ArrayBuffer[(Long,Double)]() iter => { val scoreAndLabelMap = HashMap[String, Array[(Double, Double)]]() for (row scoreAndLabelArray) } else { var scoreAndLabelArray = Array[(Double, Double)]() scoreAndLabelArray :+= ((score, label)) scoreAndLabelMap += (id -> scoreAndLabelArray) } } val users = scoreAndLabelMap.keys for (user ((x._1 + y._1),(x._2 + y._2))) val totalImpression = result._1 val totalAUC = result._2 println(s"totalImpression = ${totalImpression}") println(s"totalAUC = ${totalAUC}") val gauc = if (totalImpression != 0) (totalAUC / totalImpression.toDouble).formatted("%.8f").toDouble else 0.0d println(s"GAUC = ${gauc}") gauc } def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val scoreAndLabels = scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[(Double, Double)]() scoreAndLabels += ((0.4, 1)) scoreAndLabels += ((0.4, 0)) scoreAndLabels += ((0.3, 0)) scoreAndLabels += ((0.35, 0)) scoreAndLabels.toArray val roc_line = roc(scoreAndLabels.toArray) println(roc_line.mkString(",")) val auc_value = areaUnderROC(roc_line) println(auc_value) } ``` 代码已经测试可用,希望对大家有用。 python版的代码可以参考: https://github.com/qiaoguan/deep-ctr-prediction/blob/master/DeepCross/metric.py <ins class="adsbygoogle" style="display:block; text-align:center;" data-ad-layout="in-article" data-ad-format="fluid" data-ad-client="ca-pub-4353345653789615" data-ad-slot="8840342077"></ins>