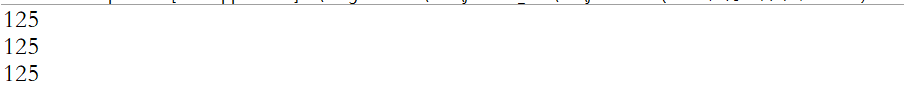目录
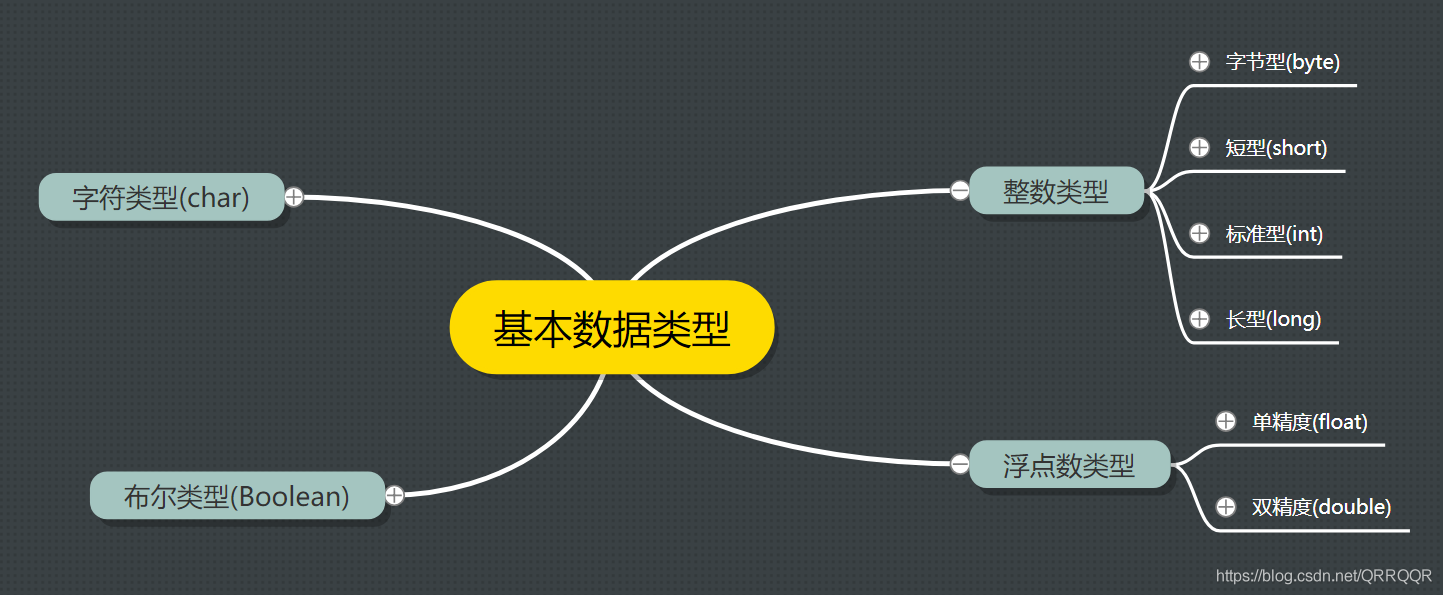
一.Java的基本数据类型介绍
| 类型 | 关键字 | 位数 | 默认值 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 字节型 | byte | 8 | 0 | -128~127 |
| 短整型 | short | 16 | 0 | -32768~32767 |
| 整型 | int | 32 | 0 | -2147483648~2147483647 |
| 长整型 | long | 64 | 0 | -9223372036854775808~ 9223372036854775807 |
| 单精度浮点型 | float | 32 | 0.0F | -3.40282347E+38~3.40282347E+38 |
| 双精度浮点型 | double | 64 | 0.0D | -1.79769313486231570E+308~ 1.79769313486231570E+308 |
| 字符型 | char | 16 | '\u0000' | '\u0000'~'\uFFFF' |
| 布尔型 | boolean | 8 | false | true,false |
二.各类基本数据之间的转换
1.自动转换(它只能按优先关系将位数少的数据类型向位数多的数据类型转换)
Byte、short、char → int → long → float → double
数据类型自动转换规则(总结:小转大,转后即为大)
| 操作数1的数据类型 | 操作数2的数据类型 | 转换后的数据类型 |
|---|---|---|
| Byte、int | int | int |
| Byte、short、int | long | long |
| Byte、short、int、long | float | float |
| Byte、short、int、long、float | double | double |
| char | int | int |
代码:(byte,short,char之间不会相互转换,他们三者在计算时首先转换为int类型)
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = 'h';
byte b = 6;
int i = 100;
long l = 567L;
float f = 8.99f;// 单精度小数需用F或f为后缀
double d = 4.7788;// 双精度小数可用D、d或不加后缀表示
int aa = c + i;// c自动转换为int类型再运算
long ll = l - aa;// aa自动转换为long类型再运算
float ff = b * f;// b自动转换为float类型再运算
double dd = ff / aa + d;// aa自动转换为float类型运算,ff/aa得float结果后再自动转换为double类型再进行运算
System.out.println("aa=" + aa);
System.out.println("ll=" + ll);
System.out.println("ff=" + ff);
System.out.println("dd=" + dd);
}
}结果:
2.强制转换:将高级数据转换成低级数据(其中的char类型与int类型转换有些特殊)
格式:要求强制转换的变量名前面用( )括上所要强制转换的类型符
代码:
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = 'h';
byte b = 6;
int i = 100;
long l = 567L;
float f = 8.99f;// 单精度小数需用F或f为后缀
double d = 4.7788;// 双精度小数可用D、d或不加后缀表示
int ii=(int)l;//将long型的l强制转换为int型的ii
long ll=(long)f;//将float型的f强制转换为long型的ll
int cc=(int)c;//将char型的c强制转换为int型的cc
System.out.println("ii=" + ii);
System.out.println("ll=" + ll);
System.out.println("cc=" + cc);
}
}
结果:
- 【问题来了】:当char型数字想要转换为int型或int型转换为char型还用同样方法可以吗?答案是:NO!
若仍使用同样方法则:当char型数字自动转换为int型,其结果为char型数字的ASCII码。
当int型数字转换为char型则得不出结果
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = '8';
int i = 9;
int b1 = c;//将char型数字自动转换为int型
char cc1 = (char) i;//将int型数字强行转换为char型
System.out.println("b1=" + b1);//56,即8的ASCII码
System.out.println("cc1=" + cc1);//没有结果
}
}
结果:
解决方案:
由char型数字转int型,给字符减'0'即可
由int型转char型,给数字加'0'并强制转换即可
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char c = '8';
int i = 9;
int b = c - '0';//由char型转int型,给字符减'0'即可
char cc = (char) (i + '0');//由int型转char型,给数字加'0'并强制转换即可
System.out.println("b=" + b);
System.out.println("cc=" + cc);
}
}结果:
三.基本数据类型和String之间转换(附:对象包装类及所对应的基本数据类型)
| 对象包装类 | 基本数据类型 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | boolean |
| Byte | byte |
| Character | char |
| Short | short |
| Integer | int |
| Long | long |
| Float | float |
| Double | double |
1.字符串→基本数据类型(以字符串→int型,float型为例)
- 调用包装类的 对应的包装类.parsexxx 方法
- 调用包装类的 对应的包装类.valueOf() 方法
类似地,由字符串→其它基本数据类型之间转换也可使用此方法。
例子:
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "12345678";
int a = Integer.parseInt(str);//第一种方法
int a1 = Integer.valueOf(str);//第二种方法
float f = Float.parseFloat(str);//第一种方法
float f1=Float.valueOf(str);//第二种方法
System.out.println(a);//12345678
System.out.println(a1);//12345678
System.out.println(f);//1.2345678E7
System.out.println(f1);//1.2345678E7
}
}结果:
2.基本数据类型→字符串(以int型→字符串为例)
- 用一个空字符串加上基本类型,得到的就是基本类型数据对应的字符串
- 使用String类的 String.valueOf() 方法
- 使用包装类的 对应的包装类.toString() 方法
类似地,由其它基本数据类型→字符串之间转换也可使用此方法。
例子:
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 125;
String str = " ";//方法一
String str1 = a + str;//方法二
String str2 = String.valueOf(a);//方法三
String str3 = Integer.toString(a);
System.out.println(str1);//125
System.out.println(str2);//125
System.out.println(str3);//125
}
}结果:
四.String与字符数组转换
1.字符数组→字符串
- public static String valueOf(char[]) 用字符数组中的全部字符创建字符串对象。
- public static valueOf String(char[],int offset,int count) 用字符数组中的全部字符和部分字符创建字符串对象。(注:data - 字符数组。offset - String 的索引【字符串索引从0开始】。count - String 值的长度。)
- String(char[]) 用字符数组中的全部字符创建字符串对象。
- String(char[],int offset,intlength) 用字符数组中的部分字符创建字符串对象。
例子:
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] arr = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' };
String str = String.valueOf(arr);//第一种方法
String str1=String.valueOf(arr, 0, 3);//第二种方法
String str2 =new String(arr);//第三种方法
String str3=new String(arr, 0, 3);//第四种方法
System.out.println(str);//hello
System.out.println(str1);//hel(其中不包含下标为3的字符)
System.out.println(str2);//hello
System.out.println(str3);//hel(其中不包含下标为3的字符)
}
}
结果:
2.字符串→字符数组
- public char[] toCharArray():将字符串中的全部字符存放在一个字符数组中的方法。
- public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin):提供了将指定索引范围内的字符串存放到数组中的方法
例子:
package Sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[ ] arr = new char[4];
char[ ] arr1 = new char[3];
String str = "hello";
arr=str.toCharArray();
str.getChars(0, 3, arr1, 0);//要复制的第一个字符位于索引 srcBegin 处; 要复制的最后一个字符位于索引 srcEnd-1 处(因此要复制的字符总数是srcEnd-srcBegin)。 要复制到 dst 子数组的字符从索引 dstBegin 处开始,并结束于索引: dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));//[h, e, l, l, o]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));//[h, e, l]
}
}结果:
五.String与字节数组转换
1.字节数组→字符串
- String(byte[]):通过使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的 byte 数组,构造一个新的 String。
- String(byte[],int offset,int length) :用指定的字节数组的一部分,即从数组起始位置offset开始取length个字节构造一个字符串对象。
例子:
package Sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] arr = { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' };
String str1=new String(arr);//第一种方法
String str2=new String(arr, 0, 3);//第二种方法
System.out.println(str1);//hello
System.out.println(str2);//hel(其中不包含下标为3的字符)
}
}
2.字符串→字节数组
- public byte[] getBytes() :使用平台的默认字符集将此 String 编码为byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。
- public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) :使用指定的字符集将此 String 编码到 byte 序列,并将结果存储到新的 byte 数组。注:charsetName为编码字符集
例子:
package Sort;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class practice {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
byte[] arr = new byte[4];
byte[] arr1 = new byte[4];
String str = "hello";
arr = str.getBytes();//第一种方法
arr1 = str.getBytes("UTF-8");//第二种方法
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));// [104, 101, 108, 108, 111]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));// [104, 101, 108, 108, 111]
}
}
结果:
到此我们各种类型的转换就全部写完啦~
如果你觉得这篇文章还不错,麻烦帮我点个赞!可以让更多人看到这篇文章。让我有动力继续更技术文~
关注小乔的公众号【小乔的编程内容分享站】,更多的Java资源干货等你来学哦~