输入与输出
Linux系统将每个对象当作文件处理,这包括输入和输出进程。
Linux用文件描述符来标识每个文件对象。
文件描述符是一个非负整数,可以唯一标识会话中打开的文件。
每个进程一次多可以有九个文件描述符。出于特殊目的,bash shell保留了前三个文件描述符(0、1和2)
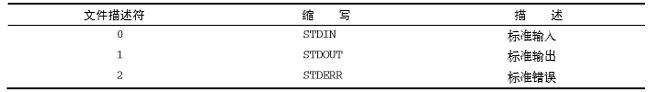
这三个特殊文件描述符会处理脚本的输入和输出。
1、stdin
STDIN文件描述符代表shell的标准输入
在使用输入重定向符号(<)时,Linux会用重定向指定的文件来替换标准输入文件描述符。 它会读取文件并提取数据,就如同它是键盘上键入的。
[root@node1 ljy]# cat < one.txt one two three
2、stdout
STDOUT文件描述符代表shell的标准输出
[root@node1 ljy]# date > time.txt [root@node1 ljy]# more time.txt 2019年 05月 16日 星期四 10:08:51 CST [root@node1 ljy]# date >> time.txt #>>表示追加的意思 [root@node1 ljy]# more time.txt 2019年 05月 16日 星期四 10:08:51 CST 2019年 05月 16日 星期四 10:09:01 CST
3、stderr
shell通过特殊的STDERR文件描述符来处理错误消息。
默认情况下,错误消息也会输出到显示器输出中。
[root@node1 ljy]# aaaa 2> err.txt [root@node1 ljy]# more err.txt -bash: aaaa: 未找到命令 #shell会只定向错误消息而非普通的数据。
如果想要同时定义普通与错误的消息可以用两个重定向符的方式:
[root@node1 ljy]# ls -al one two 2> err.txt 1> normal.txt [root@node1 ljy]# more err.txt ls: 无法访问two: 没有那个文件或目录 [root@node1 ljy]# more normal.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 5月 16 10:17 one
bash也提供了特殊的重定向符实现这一个效果&>。
[root@node1 ljy]# ls -al one two &> ceshi.txt [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.txt ls: 无法访问two: 没有那个文件或目录 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 5月 16 10:17 one #生成的所有输出都会到同一位置,包括普通与错误。默认错误消息会处于更高的优先级,方便查看。
脚本中重定向输出
1、临时重定向
希望在脚本中生成错误的信息的话,可以单独的一行输出重定向到STDERR。重定向到文件描述时,你必须在文件描述符数字前加一个&符号。
[root@node1 ljy]# more one.sh #!/bin/bash echo "this is a error message!" >&2 echo "this is a normal message!" [root@node1 ljy]# sh one.sh this is a error message! this is a normal message! [root@node1 ljy]# sh one.sh 2> err.log this is a normal message! [root@node1 ljy]# more err.log this is a error message!
默认情况下,Linux会将STDERR导向STDOUT,但是运行脚本时重定向了STDERR,脚本中所有导向STDERR的都会被重新导向。
2、永久重定向
如果脚本中有大量数据需要重定向,可以使用exec命令告诉shell在脚本执行期间重定向某个特定文件描述符。
[root@node1 ljy]# more one.sh #!/bin/bash exec 1> normal.txt exec 2> err.txt echo "this is a error message!" >&2 echo "this is a normal message!" [root@node1 ljy]# [root@node1 ljy]# sh one.sh [root@node1 ljy]# ls err.txt normal.txt one.sh [root@node1 ljy]# more err.txt this is a error message! [root@node1 ljy]# more normal.txt this is a normal message!
脚本中重定向输入
exec命令允许你将STDIN重定向到linux文件中
[root@node1 ljy]# more test one two three [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bash exec 0< test count=1 while read line do echo "$count:$line" count=$[$count + 1] done [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh 1:one 2:two 3:three
阻止命令输出
shell输出到null文件的任何命令都不会被保存!
在Linux系统中null的标准位置是/dev/null,你重定向到该位置的文件都会被丢掉不会显示。
[root@node1 ljy]# ls -al > /dev/null [root@node1 ljy]# more /dev/null
也可以将/dev/null作为输入文件,可以用它来快速清空现有文件的数据,而不需要删除后重新创建。
[root@node1 ljy]# more test one two three [root@node1 ljy]# cat /dev/null > test [root@node1 ljy]# more test
创建临时文件
系统上的任何账户都有权限读写/tmp目录中的文件
mktemp可以在本地目录中创建一个临时文件,需要制定一个文件名,末尾需要设置6个X
[ljy@node1 tmp]$ mktemp ceshi.XXXXXX ceshi.vyBZEx
-t选项会强制mktemp命令在系统的临时目录创建文件。
由于mktemp命令返回来了全路径名,你可以在Linux系统的任何目录下引用该临时文件,不需要管目录在哪。
[ljy@node1 /]$ mktemp -t ceshi.XXXXXX /tmp/ceshi.eSU3MD
-d选项告诉mktemp命令来创建一个临时目录而不是一个文件。
[ljy@node1 tmp]$ mktemp -d ceshi.XXXXXX ceshi.9JVceD
记录消息
tee命令相当于管道的一个T型接头。他将从STDIN过来的数据同时发往两处,一处是STDOUT,另一处是tee命令行所指定的文件名。
[root@node1 ljy]# date | tee ceshi 2019年 05月 16日 星期四 13:57:40 CST [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi 2019年 05月 16日 星期四 13:57:40 CST
tee命令会在每次使用时覆盖输出内容,如果你想要追加,必须使用-a参数。
